Beacon Networks and Aggregators¶
Although a Beacon can be instantiated as stand-alone solution Many Beacon instances will be part of managed networks, e.g. multi-institunional projects where individual beacons are combined through a single interface. Additionally, open beacon instances may be accessed from aggregators which can register these resources, federate queries and aggregate the responses, possibly without any direct support from the instances' maintainers.
Beacon Networks
... are collections of multiple beacon instances - possibly from different institutions or providers. Beacon networks rely on some sort of central service managing the integration of nodes and provide a unified access through a customized interface and possibly with active alignment of the instances' features (such as harmonized filtering terms). One may think of a beacon network as a "managed aggregator" with some active alignment of the individual resources.
Beacon Aggregator
... provides a single interface and API for accessing multiple Beacon instances where the individual beacons may not necessarily be harmonized (or even aware of their integration through the aggregator). An aggregator may include functionality to remap requests and responses for beacons with e.g. different versions or such using different standards (genome editions, ontology terms...).
The Beacon framework includes several features aimed to be consumed by Beacon network aggregators. For example, a Beacon endpoint declares which entities are implemented in that particular instance, which filtering terms are being supported or the URL endpoints through which different entities (such as biosamples or genomic variants) can be queried.
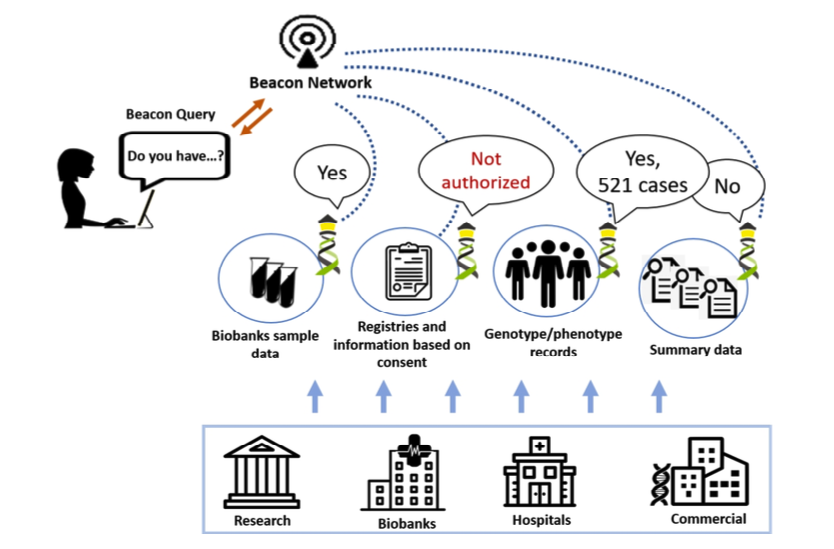
Networking heterogeneous beacons¶
In addition to genomic variation queries with Boolean responses the Beacon v2 protocol permits the implementers to support different types of entities (e.g. biosample and analysis data) both to be queried against and to be returned in Beacon responses - so a request may retrieve information about the samples in which an indicated genomic variant had been found or information about technical parameters used to detect such a variant.
However, individual beacons will have different profiles regarding the supported parameters, supported entities or the filtering terms recognized. Here, a number of information endpoints allow the profiling of beacons which is especially important when designing Beacon networks and aggregating their responses.
Supported filters¶
Filters represent a powerful way to query various features
in beacon entities. When designing a network of multiple beacons the
filtering_terms informational endpoints
can be utilized to e.g. implement translators for harmonizing the possibly differing
terms used in the individual Beacon instances.
TBD